Fed Chair Jerome Powell has been insistent that the central bank will lower inflation to 2%.
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is the primary way the Bureau of Labor Statistics measures the change in consumer prices, and the Fed watches this data closely to make some of their decisions.
“We are resolute in our goal to fight inflation… we have the tools to bring it down to 2%” are just some of the public comments coming from his office.
Should we believe him? After all, he said last year that inflation would be transitory, interest rates wouldn’t rise until 2024, and a recession is “unlikely” (or worse).
As an analyst I like to ask questions. So…
- How successful has Powell been at lowering the CPI since they started aggressively raising rates?
- Are the current circumstances surrounding inflation likely to be resolved from higher interest rates?
- What does history say about hiking rates to lower inflation?
Let’s answer each of those questions and see what we find…
Has Hiking Rates Lowered Inflation?
The first interest rate hike was in March this year.
As of the last hike, the Fed has raised interest rates 0.75% four consecutive times, what has been one of the most aggressive hike cycles in history.
How well has it worked?
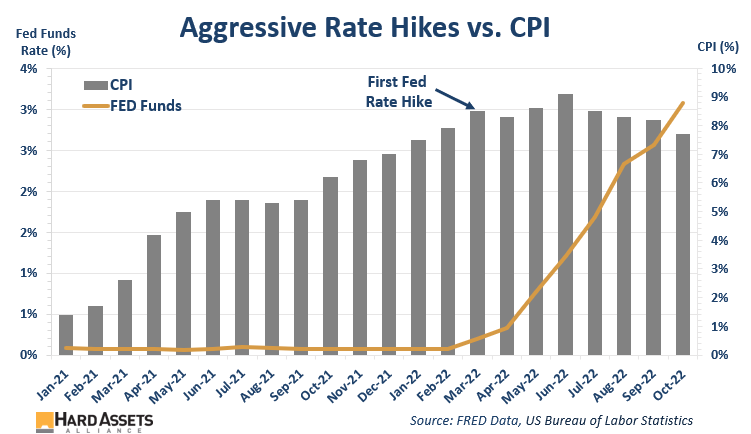
Since the Fed first raised rates 8 months ago, the CPI is down 80 basis points (about 9%).
Yes, official inflation is slightly cooling. But I’m not sure how much of that is due to the Fed’s efforts vs. a slowing economy.
You can also tell from the chart that if the central bank was truly serious about taming inflation, it could’ve started raising rates a year earlier, when it started spiking.
Either way, to get the CPI to 2% would require it to fall by 74% from the latest reading. That’s a big drop.
Let’s be honest… despite the slightly lower reading…
- The CPI has a loooong way to go to get to 2%.
Let’s ask our next question…
Can Inflation’s Root Cause Be Solved with Higher Rates?
Is aggressively hiking rates the correct prescription for the circumstances that have caused the spike in inflation?
Inflation is usually a demand-driven phenomenon. But that’s not what’s happening in this inflation cycle…
As most people know, the root cause of spiking prices centers largely around “supply chain” issues.
It kicked in last year, but it’s still going on. Based on various sources, shortages with food products including toilet paper and baby formula will continue, along with any electronic item that requires a semiconductor chip, including vehicles.
Transportation of freight is still disrupted, too — shipping, air, and rail. And now we have geopolitical conflicts we didn’t have a year ago to clog it up even more.
So, the natural question is, does pushing rates higher solve the supply chain issue?
Of course not; it likely makes it worse, since it makes doing business more expensive, since the cost of borrowing goes up.
It is true that as higher rates push demand down, the supply chain can catch up. And this appears to be underway to some degree, as surveys show that traveling, eating out, and holiday budgets are now in a downtrend.
But it’s a global economy, and when China reopens, we’re likely to see demand spike again.
Either way…
- Until supply chain issues are fully resolved, it will be extremely difficult to push the CPI down to 2%.
Does History Show Higher Rates Lower Inflation?
There’s a clear message from history about the Fed’s strategy to conquer a high CPI.
Raising rates to lower inflation does NOT happen quickly.
Most people know inflation spiked in the 1970s. Paul Volcker was hired in 1979 to bring it down. He’s remembered for being particularly aggressive in hiking rates to deal with the stubbornly high CPI—but look how long it took him.
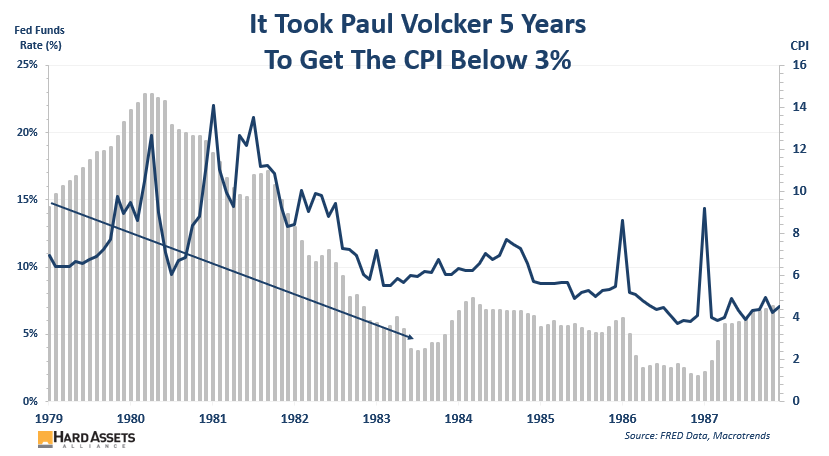
The CPI continued to rise for over a year after he was hired. And look at the arrow… it took a whopping 5 years to get it below 3%!
You might claim inflation was much higher then—that’s true, but it’s all relative. Reducing inflation from 22% to 5% is the rough equivalent of reducing it today from 7.7% to 2%… both require the CPI to fall by over 70%.
There’s another concern looking at that chart…
After Volcker got inflation below 3%, you’ll see it spiked back up again… and took another 2½ years to fall to 2%.
So, we have historical precedence that during high inflationary cycles…
- It can occur in waves. Meaning, after it falls it’s possible there could be another spike.
- It could easily remain elevated not for months but for years, based on the last time we had high inflation.
The bottom line is that…
- It historically takes YEARS to push high inflation to low levels.
Does the Fed Have What It Takes?
In my opinion, the Fed won’t have the capacity to push the CPI all the way down to 2%. They talk tough, but I think they break something long before inflation gets down to 2%.
On top of that, there are already those within the Fed calling for a pause in rate hikes.
And don’t forget citizens and investors that will be screaming when we enter a recession or open their 401k statements.
Based on this research, the more likely scenario is…
- We have entered an inflationary cycle, where the CPI remains elevated above “normal” for years.
How should we prepare for that, and the fallout that can come from it?
One way to answer that is to look at how central banks themselves are investing…
The World Gold Council recently reported that global central bank gold buying hit a record in the third quarter. They bought almost 400 tonnes, more than double the amount compared to the previous quarter and a new quarterly record.
Not only that…
- Year-to-date, central banks have purchased 673 tonnes, more than any other year since 1967—when the dollar was backed by gold!
Why are they buying so much gold right now? What do they think is coming? Why are they not waiting until the Fed pivots?
Your answer to those questions signals what to do as an investor and a citizen.
Either way, the data show we should prepare for inflation to take a long time to fall to 2%. Prepare accordingly and make sure you have enough gold (and silver).



